Other

“Applying machine learning to find the properties of atomic pieces of geometry shows how AI has the power to accelerate discoveries in maths. Mathematicians from Imperial College London and the University of Nottingham have, for the first time, used machine …

“Imperial College London and Empa researchers have created a fleet of bee-inspired flying 3D printers for building and repairing structures in-flight. The technology could ultimately be used for manufacturing and building in difficult-to-access or dangerous locations such as tall buildings …

“Researchers have shown it is possible to perform artificial intelligence using tiny nanomagnets that interact like neurons in the brain. The new method, developed by a team led by Imperial College London researchers, could slash the energy cost of artificial …

“Imperial researchers have developed a hydrogen fuel cell that uses iron instead of rare and costly platinum, enabling greater use of the technology. Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen to electricity with water vapour as the only by-product, making them an …
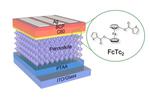
“New solar cell devices that are cheaper and easier to make could soon make their way to market thanks to materials made at Imperial College London. Traditional solar cells are made from silicon, which has good efficiency and stability, but …

“A study of electron dynamics timed to millionths of a billionth of a second reveals the damage radiation can do on a molecular level. The first-of-its kind study used ultrafast X-ray laser pulses to disrupt the electrons in a molecule …
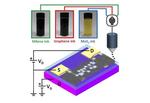
“Scientists have shown how electricity is transported in printed 2D materials, paving the way for design of flexible devices for healthcare and beyond. A study, published today in Nature Electronics, led by Imperial College London and Politecnico di Torino researchers …

“An Imperial-led team of international researchers has used a special X-ray probe to gain new insights into how electrons behave at the quantum level. Since electrons drive many chemical reactions, the method could lead to a deeper understanding of physics …
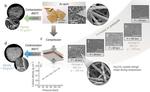
“Scientists have created a new generation of low-cost, high-energy supercapacitors to power electric vehicles. Researchers from Imperial College London and University College London (UCL) have produced a cheaper, more sustainable and energy-dense electrode material for supercapacitors which could pave the …
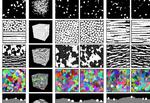
“A new algorithm developed at Imperial College London can convert 2D images of composite materials into 3D structures. The machine learning algorithm could help materials scientists and manufacturers to study and improve the design and production of composite materials like …

