Other

“Using a diamond to cut glass is not news, but a research team in northern China recently developed the world’s hardest glassy material that can leave a deep scratch on the surface of a diamond with ease. The (tentatively …

“Bacterial infections relating to medical implants place a huge burden on healthcare and cause great suffering to patients worldwide. Now, researchers at Chalmers, have developed a new method to prevent such infections, by covering a graphene-based material with bactericidal molecules …

“Curtin University researchers have found applying a thin invisible layer of graphene oxide to silicon forms an impermeable barrier, which could be used to protect artwork, prevent corrosion of metals, and produce higher efficiency solar cells. Lead author Dr Nadim …
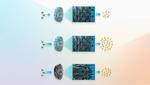
“To take advantage of the growing abundance and cheaper costs of renewable energy, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers are 3D printing flow-through electrodes (FTEs), core components of electrochemical reactors used for converting CO2 and other molecules to …
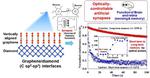
“Scientists from Japan mimic the brain’s functions with junctions between vertically aligned graphene and diamond The human brain holds the secret to our unique personalities. But did you know that it can also form the basis of highly efficient …

“New findings might help inform the design of more powerful MRI machines or robust quantum computers. MIT physicists have observed signs of a rare type of superconductivity in a material called magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene. In a study appearing today …
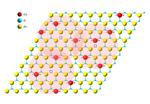
“A one-atom-thin 2D magnet developed by Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley could advance new applications in computing and electronics The development of an ultrathin magnet that operates at room temperature could lead to new applications in computing and electronics – such …

“A new mathematical model helps predict the tiny changes in carbon-based materials that could yield interesting properties. Scientists at Tohoku University and colleagues in Japan have developed a mathematical model that abstracts the key effects of changes to the geometries …

“A scattering-type scanning nearfield optical microscope offers advantages to researchers across many disciplines. An MIT physicist has built a new instrument of interest to MIT researchers across a wide range of disciplines because it can quickly and relatively inexpensively determine …
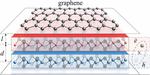
“Placing a 2D Bose-Einstein condensate in the vicinity of a graphene layer confers superconductivity to the material Superconductivity is a physical phenomenon where the electrical resistance of a material drops to zero under a certain critical temperature. Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory …