Other

“MIT chemists developed a battery cathode based on organic materials, which could reduce the EV industry’s reliance on scarce metals. Many electric vehicles are powered by batteries that contain cobalt — a metal that carries high financial, environmental, and social …
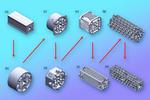
“Lightweight and inexpensive, miniaturized mass filters are a key step toward portable mass spectrometers that could identify unknown chemicals in remote settings. Mass spectrometers, devices that identify chemical substances, are widely used in applications like crime scene analysis, toxicology testing …

“A CSAIL study highlights why it is so challenging to program a quantum computer to run a quantum algorithm, and offers a conceptual model for a more user-friendly quantum computer. When MIT professor and now Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence …
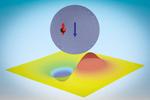
“Study shows neutrons can bind to nanoscale atomic clusters known as quantum dots. The finding may provide insights into material properties and quantum effects. Neutrons are subatomic particles that have no electric charge, unlike protons and electrons. That means that …
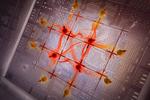
“The advance offers a way to characterize a fundamental resource needed for quantum computing. Entanglement is a form of correlation between quantum objects, such as particles at the atomic scale. This uniquely quantum phenomenon cannot be explained by the laws …

“Screen-reader users can upload a dataset and create customized data representations that combine visualization, textual description, and sonification. A growing number of tools enable users to make online data representations, like charts, that are accessible for people who are blind …

“Mass spectrometry, a technique that can precisely identify the chemical components of a sample, could be used to monitor the health of people who suffer from chronic illnesses. For instance, a mass spectrometer can measure hormone levels in the blood …

“A system designed at MIT could allow sensors to operate in remote settings, without batteries. MIT researchers have developed a battery-free, self-powered sensor that can harvest energy from its environment. Because it requires no battery that must be recharged or …

“The advance could help make 3D printing more sustainable, enabling printing with renewable or recyclable materials that are difficult to characterize. While 3D printing has exploded in popularity, many of the plastic materials these printers use to create objects cannot …

“The device, based on simple tetromino shapes, could determine the direction and distance of a radiation source, with fewer detector pixels. The spread of radioactive isotopes from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011 and the ongoing …

