Other

“From cars to cans, we are surrounded by the enduring silvery shine of aluminium. We asked metallurgist Casper van der Eijk what makes it worth its weight in gold. Despite being the most abundant metal on Earth, constituting over 8 …

“The MESO-BRAIN project used human-induced pluripotent stem cells placed on nanoscale 3D-laser-printed structures to replicate the brain’s neural networks 3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, has become widespread in recent years. By building successive layers of raw material …
“If computers transmitted data using photons instead of electrons, they would perform better and devour less power. European researchers are now studying a new light-emitting alloy of silicon and germanium to obtain photonic chips, which can revolutionise computing. Over the …

“Hybrid and electric vessels are under the spotlight lately, thanks to intensified efforts to limit greenhouse gas emissions from global shipping, a significant source of CO2 and other pollutants. There are already several offerings of such green ships in Europe …

“European engineers have developed a novel generator that could be used to power thousands of homes. Ocean waves hold a tremendous amount of untapped energy that is more than capable of meeting the world’s electricity needs. However, electricity generation …

“Graphene is a two-dimensional atomic crystal made up of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. At one atom thick, graphene is the thinnest known compound, as well as the strongest compound discovered (between 100 and 300 times stronger than …
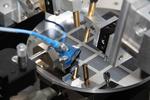
“Integrating graphene sheets into silicon photonics could form the basis for next-generation data communications. Researchers from the Graphene Flagship initiative have pushed the technology closer to application by demonstrating the world’s first high-speed graphene-based data communication at a data …
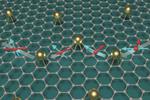
“Graphene Flagship researchers produced graphene-based spintronics devices that utilise both electron charge and spin at room temperature. Demonstrating the spin’s feasibility for bridging distances of up to several micrometres, results open up new possibilities for integrating information-processing and storage …

“Pollution is a serious issue in many parts of the world, especially in urban areas. Using novel graphene-based materials, researchers from the Graphene Flagship Functional Foams and Coatings Work Package have provided solutions to tackle environmental contamination, among other applications …

“Researchers achieve world-first data transmission capacity for 5G and next-generation networks. We use the Internet in nearly every aspect of our daily lives – when making video calls, telecommuting, playing online interactive games, interacting on social networks or using smart TVs …

