Other

“A replacement for cobalt in batteries avoids its environmental and social impacts High-capacity and reliable rechargeable batteries are a critical component of many devices and even modes of transport. They play a key role in the shift to a greener …

“3D printing of complex objects typically takes a long time due to the printing process necessarily laying down a large number of 2D layers to build up the object. The process usually wastes a lot of material required to support …
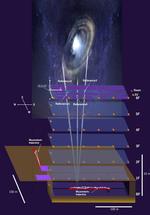
“Superfast, subatomic-sized particles called muons have been used to wirelessly navigate underground in a reportedly world first. By using muon-detecting ground stations synchronized with an underground muon-detecting receiver, researchers at the University of Tokyo were able to calculate the receiver …
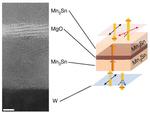
“Room temperature quantum magnets switch states trillions of times per second A class of nonvolatile memory devices, called MRAM, based on quantum magnetic materials, can offer a thousandfold performance beyond current state-of-the-art memory devices. The materials known as antiferromagnets were …

“The manufacturing industry is constantly on the lookout for more efficient manufacturing materials, but most new methods to develop such materials created in the lab are not suited for industrial-scale use. Now, investigators from The Institute of Industrial Science at …
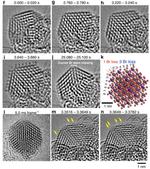
“Quantum dots are nanoscale crystals capable of emitting light of different colors. Display devices based on quantum dots promise greater power efficiency, brightness and color purity than previous generations of displays. Of the three colors typically required to display full …

“Computers that can make use of the “spooky” properties of quantum mechanics to solve problems faster than current technology may sound alluring, but first they must overcome a massive disadvantage. Scientists from Japan may have found the answer through their …

“High-temperature and high-pressure experiments involving a diamond anvil and chemicals to simulate the core of the young Earth demonstrate for the first time that hydrogen can bond strongly with iron in extreme conditions. This explains the presence of significant amounts …
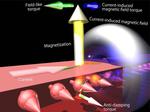
“Memory based on the physics of spintronics could offer high speeds at low power Researchers are a step closer to realizing a new kind of memory that works according to the principles of spintronics which is analogous to, but different …
“A new and efficient way to create nanographene for power and display devices. Nanographene is a material that is anticipated to radically improve solar cells, fuel cells, LEDs and more. Typically the synthesis of this material has been imprecise and …

