Other

“All-solid-state lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries with solid electrolytes are non-flammable and have higher energy density and transference numbers than those with liquid electrolytes. They are expected to take a share of the market for conventional liquid electrolyte Li-ion batteries, such as …
“Annealing processors are designed specifically for addressing combinatorial optimization problems, where the task is to find the best solution from a finite set of possibilities. This holds implications for practical applications in logistics, resource allocation, and the discovery of drugs …

“Researchers employ a new “transmetallation” technique to develop ultrathin electronic devices from 2D coordination nanosheets. Electronically conducting two-dimensional (2D) materials are currently hot topics of research in both physics and chemistry owing to their unique properties that have the potential …
News Optical-Fiber based Single-Photon Light Source at Room Temperature for Next-Generation Quantum Processing

“Quantum-based systems promise faster computing and stronger encryption for computation and communication systems. These systems can be built on fiber networks involving interconnected nodes which consist of qubits and single-photon generators that create entangled photon pairs. In this regard, rare-earth …

“The demand for efficient energy storage systems is ever increasing, especially due to the recent emergence of intermittent renewable energy and the adoption of electric vehicles. In this regard, lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs), which can store three to five times more …
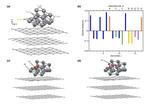
“Scientists have elucidated the reason for the new catalyst’s high activity, which is 2.1 times higher than commercial platinum nanoparticle-based catalysts Hydrogen, derived from polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs), is an excellent source of clean energy. However, PEFCs …

“Lithium-ion batteries have remained unrivaled in terms of overall performance for several applications, as evidenced by their widespread use in everything from portable electronics to cellular base stations. However, they suffer from few important disadvantages that are difficult to ignore …
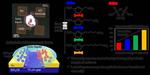
“Researchers from Japan design a tunable physical reservoir device based on the dielectric relaxation at an electrode-ionic liquid interface Physical reservoir computing (PRC), which relies on the transient response of physical systems, is an attractive machine learning framework that can …

“Scientists from Japan have quantitatively evaluated ion-trapping-induced degradation in lithium intercalated tungsten oxide films Tungsten oxide, an electrochromic (EC) material with immense potential for technical applications such as in smart windows, has attracted much interest for its energy-saving qualities. However …

“New design approach for manufacturing carbon fibers with optimized orientation and thickness achieves weight reduction in fiber reinforced plastics Carbon fibers, due to their superior strength and lightness, are popular in aerospace engineering applications. While much effort goes into improving …

“Scientists design a novel quantum circuit that calculates the fast Fourier transform, an indispensable tool in all fields of engineering. The Fourier transform is a mathematical operation essential to virtually all fields of physics and engineering. Although there already exists …

“New insight into the spin behavior in an exotic state of matter puts us closer to next-generation spintronic devices The quantum spin liquid (QSL) state is an exotic state of matter where the spin of electrons, which generally exhibits order …

“Scientists conduct numerical simulations on complex networks to gain insight into a powerful quantum mechanics-inspired algorithm Complex networks are ubiquitous in the real world, from artificial to purely natural ones, and they exhibit very similar geometric properties. Algorithms based on …

