Other
“An international team of researchers from Queen Mary University of London, the University of Oxford, Lancaster University, and the University of Waterloo have developed a new single-molecule transistor that uses quantum interference to control the flow of electrons. The transistor …
News New study finds ways to suppress lithium plating in automotive batteries for faster charging electric vehicles

“A new study led by Dr. Xuekun Lu from Queen Mary University of London in collaboration with an international team of researchers from the UK and USA has found a way to prevent lithium plating in electric vehicle batteries, which …
News Atomically-thin ribbons can dramatically improve batteries needed for clean transport, as well as solar power

“PNRs are ribbon-like strands of the 2D material phosphorous, which, like graphene, are made of single-atom-thick layers of atoms. They were first created in 2019 by a team led by Professor Chris Howard of UCL following over a hundred theoretical …
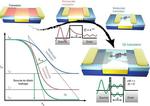
“Due to their very high efficiency in transporting electric charges from light, perovskites are known as the next generation material for solar panels and LED displays. We now have invented a brand-new application of perovskites as optical fibres. The results …

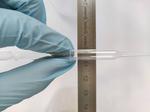
“Researchers have created a simple Covid-19 testing lab that fits into a backpack providing a cheap and effective solution for low income or remote areas. In a new study, published in PLOS ONE, scientists from Queen Mary University of London …

“A new study, published in the journal Advanced Optical Materials, is the first to show graphene can replace Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) in an electronic or optical device. Researchers from Paragraf and Queen Mary University of London demonstrated the successful …
“A research collaboration between Queen Mary University of London, the University of Cambridge and the Institute for High Pressure Physics in Troitsk has discovered the fastest possible speed of sound. The result- about 36 km per second - is around twice …
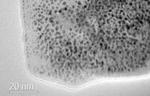
“In the study, published today in the journal Nanoscale, researchers produced graphene via a special, scalable technique and used it to develop hydrogen fuel cell catalysts. They showed that this new type of graphene-based catalyst was more durable than commercially …

“In the study, published in the journal Physical Review B, the researchers showed that bilayer graphene, consisting of two layers of graphene, was noticeably softer than both two-dimensional (2D) graphene and three-dimensional (3D) graphite along the stacking direction. This surprising …

“Einstein’s theory of Brownian motion, which describes the random movement of particles in fluids, is widely used to model randomness throughout science. However, this revolutionary model only works when a fluid is static, or at equilibrium. In real-life environments …

