Other

“Electrons hold the world together. When chemical reactions yield new substances, they play a leading role. And in electronics, too, they are the protagonists. Together with his colleagues, Ferenc Krausz, Director of the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics in …
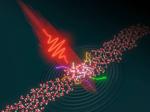
“The behavior of electrons in liquids determines a vast range of chemical processes and thus essential processes in organisms and the world as a whole. But electron movements are extremely hard to capture because they take place within attoseconds: the …

“Using a metabolic pathway, energy-rich resources can be produced via the power of electricity When nature performs chemical reactions to create energy-rich compounds from simple molecules, it requires energy. So far, it has not been possible to use human-made electricity …

“Special shapes can release active substances in a controlled manner. Pills could soon be produced in shapes that resemble design objects. And this would not be just an aesthetic gimmick, but would serve to release active medical ingredients in the …

“How an exoplanet survived the rebellion of its home star. When stars, similar to the sun, have reached the end of their lifetime, they inflate into red giant stars. The sun, for example, would then have a diameter hundreds of …

“Precise as a clock: pulsars in the Milky Way form large-scale observatory for gravitational waves Astronomical observatories are usually based on Earth and study the extreme processes in the universe by capturing light as an information carrier. But not all …

“Understanding how short-circuits occur in solid-state batteries could extend their lifespan They could be the next generation of battery: so-called ‘solid-state’ batteries. They’re made entirely of solid materials and have no liquid medium between their poles, as today’s …

“Most of the world is covered in oceans, which are unfortunately highly polluted. One of the strategies to combat the mounds of waste found in these very sensitive ecosystems — especially around coral reefs — is to employ robots to master the …

“They are considered the “Holy Grail” of battery research: so-called “solid-state batteries”. They no longer have a liquid core, as is the case with today’s batteries, but consist of a solid material. This leads to several advantages: Among other …

“Scientists assemble matter in 3D using sound waves for 3D printing Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research and the Heidelberg University have created a new technology to assemble matter in 3D. Their concept uses multiple acoustic holograms …

