Other
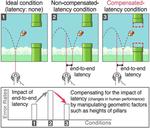
“One of the most challenging issues for game players looks to be resolved soon with the introduction of a zero-latency gaming environment. A KAIST team developed a technology that helps game players maintain zero-latency performance. The new technology transforms the …

“When we think about clothes, they are usually formed with textiles and have to be both wearable and washable for daily use; however, smart clothing has had a problem with its power sources and moisture permeability, which causes the devices …
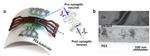
“A KAIST research team developed a technology that makes a transition of the operation mode of flexible memristors to synaptic analog switching by reducing the size of the formed filament. Through this technology, memristors can extend their role to memristive …

“A KAIST research team developed a silicon optical phased array (OPA) chip, which can be a core component for three-dimensional image sensors. This research was co-led by PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kim and Dr. Jong-Bum You from the National Nanofab Center …
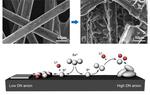
“A KAIST research team has developed a lithium sulfur battery (LSB) that realizes 92% of the theoretical capacity and an areal capacity of 4mAh/cm2. LSBs are gaining a great deal of attention as an alternative for lithium ion batteries …

“The next generation of flexible and transparent displays will require a high-performing and flexible polymeric material that has the optical and thermal properties of glass. The material must be transparent to visible light and have a low coefficient of thermal …

“Flexible, wireless electronic devices are rapidly emerging and have reached the level of commercialization; nevertheless, most of battery shapes are limited to either spherical and/or rectangular structures, which results in inefficient space use. Professor Il-Doo Kim’s team from …

“Producing effective epidermal electronics requires a strong, biocompatible interface between a biological surface and a sensor. Here, a KAIST team employed a calcium-modified silk fibroin as a biocompatible and strong adhesive. This technology led to the development of epidermal electronics …

“A KAIST research team made it one step closer to realizing safe energy storage with high energy density, high power density, and a longer cycle life. This hybrid storage alternative shows power density 100 times faster than conventional batteries, allowing …

“The use of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) has extended to various applications, but their efficiency is still lagging behind inorganic light-emitting diodes. In this research, a KAIST team provided a systematic way to yield OLEDs with an external quantum efficiency …
