“Physicists publish a theoretical framework to explain the recent discovery of superconductivity in trilayer graphene
Since superconductivity in three-layered graphene was discovered in September, the physics community has been left puzzled. Now, three months later, physicists from IST Austria together with colleagues from the Weizmann Institute of Science can successfully explain the results by drawing from a theory of unconventional superconductivity. The work has been published in Physical Review Letters.
A single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice makes up the promising nanomaterial called graphene. Research on a setup of three sheets of graphene stacked on top of one another so that their lattices are aligned but shifted — forming rhombohedral trilayer graphene – revealed an unexpected state of superconductivity. In this state electrical resistance vanishes due to the quantum nature of the electrons. The discovery was published and debated in Nature, whilst the origins remained elusive. Now, Professor Maksym Serbyn and Postdoc Areg Ghazaryan from the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria in collaboration with Professor Erez Berg and Postdoc Tobias Holder from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, developed a theoretical framework of unconventional superconductivity, which resolves the puzzles posed by the experimental data.
The Puzzles and their Resolution
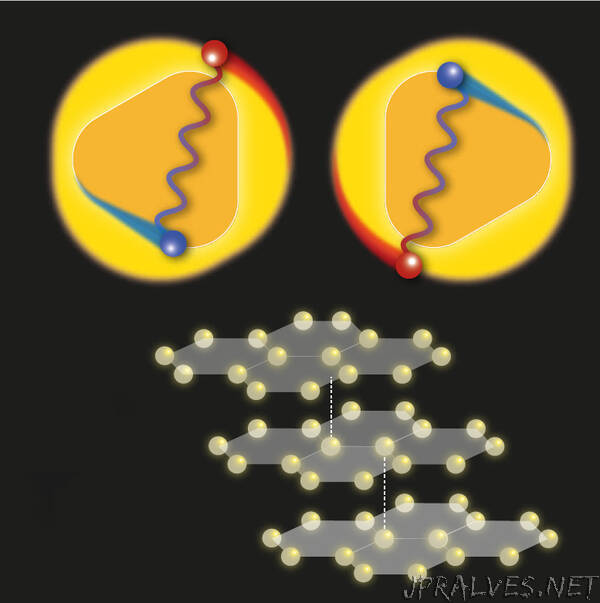
Superconductivity relies on the pairing of free electrons in the material despite their repulsion arising from their equal negative charges. This pairing happens between electrons of opposite spin through vibrations of the crystal lattice. Spin is a quantum property of particles comparable, but not identical to rotation. The mentioned kind of pairing is the case at least in conventional superconductors. “Applied to trilayer graphene,” co-lead-author Ghazaryan points out, “we identified two puzzles that seem difficult to reconcile with conventional superconductivity.”
First, above a threshold temperature of roughly -260 °C electrical resistance should rise in equal steps with increasing temperature. However, in the experiments it remained constant up to -250 °C. Second, pairing between electrons of opposite spin implies a coupling that contradicts another experimentally observed feature, namely the presence of a nearby configuration with fully aligned spins, which we know as magnetism. “In the paper, we show that both observations are explainable,” group leader Maksym Serbyn summarizes, “if one assumes that an interaction between electrons provides the ‘glue’ that holds electrons together. This leads to unconventional superconductivity.”
When one draws all possible states, which electrons can have, on a certain chart and then separates the occupied ones from the unoccupied ones with a line, this separation line is called a Fermi surface. Experimental data from graphene shows two Fermi surfaces, creating a ring-like shape. In their work, the researchers draw from a theory from Kohn and Luttinger from the 1960’s and demonstrate that such circular Fermi surfaces favor a mechanism for superconductivity based only on electron interactions. They also suggest experimental setups to test their argument and offer routes towards raising the critical temperature, where superconductivity starts appearing.
The Benefits of Graphene Superconductivity
While superconductivity has been observed in other trilayer and bilayer graphene, these known materials must be specifically engineered and may be hard to control because of their low stability. Rhombohedral trilayer graphene, although rare, is naturally occurring. The proposed theoretical solution has the potential of shedding light on long-standing problems in condensed matter physics and opening the way to potential applications of both superconductivity and graphene.
Publication
Ghazaryan, Holder, Serbyn & Berg. 2021. Unconventional superconductivity in systems with annular Fermi surfaces: Application to rhombohedral trilayer graphene. Physical Review Letters. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.247001
Funding information
The IST Austria project part was supported by funding from the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 754411. Erez Berg and Tobias Holder were supported by the European Research Council (ERC) under Grant Agreement No. 817799.”
