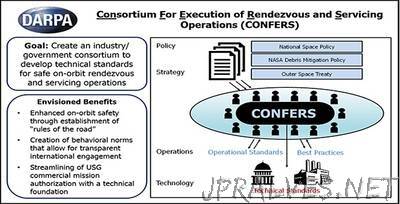
“Recent technological advances have made the longstanding dream of on-orbit robotic servicing of satellites a near-term possibility. The potential advantages of that unprecedented capability are enormous. Instead of designing their satellites to accommodate the harsh reality that, once launched, their investments could never be repaired or upgraded, satellite owners could use robotic vehicles to physically inspect, assist, and modify their on-orbit assets. That could significantly lower construction and deployment costs while dramatically extending satellite utility, resilience, and reliability. In fact, efforts to achieve the goal of on-orbit servicing are already underway, including DARPA’s Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellite (RSGS) program which focuses on services for satellites in geosynchronous orbit. But these efforts all face a major roadblock: the lack of clear, widely accepted technical and safety standards for responsible performance of on-orbit activities involving commercial satellites, including rendezvous and proximity operations (RPO) that don’t involve physical contact with satellites and robotic servicing operations that would. Without these standards, the long-term sustainability of outer space operations is potentially at risk. To help overcome these challenges and provide the foundation for a new commercial repertoire of robust space-based capabilities, DARPA is creating the Consortium for Execution of Rendezvous and Servicing Operations (CONFERS). Through CONFERS, DARPA aims to establish an industry/government forum composed of experts from throughout the space community. Participants would leverage best practices from government and industry to research, develop, and publish non-binding, consensus-derived technical and safety standards for on-orbit servicing operations. In doing so, the program would provide a clear technical basis for definitions and expectations of responsible behavior in outer space.”
