Other

“Researchers from the University of Tokyo led by doctoral student Takuya Sasatani, Disney Research and the University of Michigan in the U.S., created and demonstrated a room-sized device which uses magnetic fields to charge compatible devices inside it. “The …
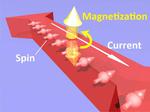
“A new low-power magnetic switching component could aid spintronic devices UTokyo researchers have created an electronic component that demonstrates functions and abilities important to future generations of computational logic and memory devices. It is between one and two orders of …

“UTokyo engineers develop a way to create high-capacity long-life batteries Engineers at the University of Tokyo continually pioneer new ways to improve battery technology. Professor Atsuo Yamada and his team recently developed a material which could significantly extend the life …

“The first data received from the Hayabusa2 spacecraft in orbit of asteroid Ryugu helps space scientists explore conditions in the early solar system. The space probe gathered vast amounts of images and other data which gives researchers clues about Ryugu …
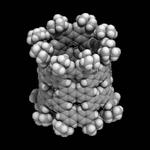
“For the first time, researchers used benzene - a common hydrocarbon - to create a novel kind of molecular nanotube, which could lead to new nanocarbon-based semiconductor applications. Researchers from the Department of Chemistry have been hard at work in their recently …

“Engineers from UTokyo and RIKEN perform computational logic with light. For the first time, researchers performed logic operations — the basis of computation — with a chemical device using electric fields and ultraviolet light. The device and the pioneering methods used open …

“Researchers from the University of Tokyo developed a new system to charge electronic devices such as smartphones and smartwatches wirelessly. The method involves a cuttable, flexible power transfer sheet which charges devices wirelessly and can be molded or even cut …
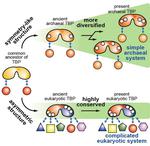
“New evolutionary indicator helps uncover ancient transcription systems Researchers at the University of Tokyo and their collaborators have revealed for the first time the mechanism by which the system that initiates transcription in eukaryotes gained complexity when organisms in this …
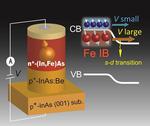
“Magnetoconductance controlled by spin-dependent band engineering Researchers at the University of Tokyo and the Tokyo Institute of Technology have successfully fabricated a spin Esaki diode composed of an n-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (FMS) indium iron arsenide (In,Fe)As—a hybrid …

“The new field of biohybrid robotics involves the use of living tissue within robots, rather than just metal and plastic. Muscle is one potential key component of such robots, providing the driving force for movement and function. However, in efforts …
