Other
“New type of transistor one step closer Electrons have a negative charge, but they also behave like tiny magnets. This property of electrons, called spin, can be used to transport or store information in electronic circuits. Scientists are looking for …
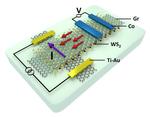
“Physicists from the University of Groningen constructed a two-dimensional spin transistor, in which spin currents were generated by an electric current through graphene. A monolayer of a transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) was placed on top of a graphene to induce …

“Study shows how ferroic materials could be used to create adaptable neuromorphic electronics A phenomenon that is well known from chaos theory was observed in a material for the first time ever, by scientists from the University of Groningen, the …
“Computer bits are binary, with a value of 0 or 1. By contrast, neurons in the brain can have all kinds of different internal states, depending on the input that they received. This allows the brain to process information in …
“An international team of scientists led by the University of Groningen’s Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials has identified a way to create quantum bits that emit photons that describe their state at wavelengths close to those used by telecom …

“University of Groningen physicists Siddhartha Omar and professor Bart van der Wees have shown that it is possible to influence the lifetime of spin in graphene. They used tungsten disulfide to induce spin orbit coupling in graphene and were able …
“Photons with energy higher than the ‘band gap’ of the semiconductor absorbing them give rise to what are known as hot electrons. The extra energy in respect to the band gap is lost very fast, as it is converted into …
