Other

“Imagine a flexible digital screen that heals itself when it cracks, or a light-emitting robot that locates survivors in dark, dangerous environments or carries out farming and space exploration tasks. A novel material developed by a team of NUS researchers …
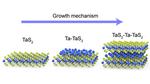
“NUS researchers have created a whole new library of atomically thin, two-dimensional (2D) materials using a novel and powerful approach of engineering the composition of transition metal dichalcogenides. Materials that are atomically thin offer a platform to explore a wide …
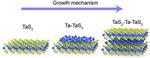
“NUS researchers have created a whole new library of atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) materials, christened “ic-2D”, to denote a class of materials based on self-intercalation of native atoms into the gap between the layers of crystals. Atomically thin two-dimensional (2D …

“NUS scientists have taken inspiration from underwater invertebrates like jellyfish to create an electronic skin with similar functionality. Just like a jellyfish, the electronic skin is transparent, stretchable, touch-sensitive, and self-healing in aquatic environments. It can be used in everything …

“A team of NUS researchers has achieved a major technological breakthrough by converting waste rubber tyres into super-light aerogels that have a wide range of applications. This is the first time that aerogels are made from waste rubber tyres. The …

“‘Origami robots’ are state-of-the-art soft and flexible robots that are being tested for use in various applications including drug delivery in human bodies, search and rescue missions in disaster environments and humanoid robotic arms. Because these robots need to be …

“Robots and prosthetic devices may soon have a sense of touch equivalent to, or better than, the human skin with the Asynchronous Coded Electronic Skin (ACES), an artificial nervous system developed by a team of NUS researchers. The new electronic …
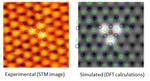
“NUS scientists have found that the oxygen interstitials in single-layer tungsten diselenide (WSe2) enable it to function as single photon emitters (SPEs) for quantum optical applications. Two-dimensional (2D) materials with atomically thin honeycomb-like lattices were recently discovered experimentally for use …
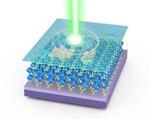
“NUS scientists have discovered that the light emission properties of molecularly thin two-dimensional (2-D) hybrid perovskite can be tuned in a highly reversible way for ultrathin optoelectronic applications. A highly efficient photodetector has been fabricated using hybrid perovskites with the …

“Researchers have discovered that using ferrimagnets can result in dramatically more stable and efficient spin-based memories A team of international researchers led by engineers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have invented a new magnetic device which is able …
