Other

“This machine-learning system can simulate how a listener would hear a sound from any point in a room. Imagine the booming chords from a pipe organ echoing through the cavernous sanctuary of a massive, stone cathedral. The sound a cathedral-goer …

“Using machine learning and simple X-ray spectra, researchers can uncover compounds that might enable next-generation computer chips or quantum devices. Topological materials, an exotic class of materials whose surfaces exhibit different electrical or functional properties than their interiors, have been …

“Researchers develop a technique for precisely arranging nanoscale particles on a surface, such as a silicon chip, that doesn’t damage the material. Researchers at MIT have developed a technique for precisely controlling the arrangement and placement of nanoparticles on …
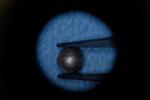
“Using a new technology, researchers hope to create better control systems for prosthetic limbs. Using a simple set of magnets, MIT researchers have come up with a sophisticated way to monitor muscle movements, which they hope will make it easier …
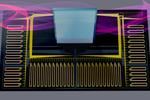
“A new method uses optics to accelerate machine-learning computations on smart speakers and other low-power connected devices. Ask a smart home device for the weather forecast, and it takes several seconds for the device to respond. One reason this latency …

“Astronomers have found a way to determine an asteroid’s interior structure based on how its spin changes during a close encounter with Earth. NASA hit a bullseye in late September with DART, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, which flew …

“The system measures biological and environmental changes, and detects contact between the mask and the wearer’s skin. Wearing a mask can help prevent the spread of viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, but a mask’s effectiveness depends on how …

“Researchers create a method for magnetically programming materials to make cubes that are very picky about what they connect with, enabling more-scalable self-assembly. While automated manufacturing is ubiquitous today, it was once a nascent field birthed by inventors such as …

“PhD student Alex Greene studies superconducting quantum computing systems while rounding out their busy schedule with water sanitation projects. In Building 13 on MIT’s campus, there sits a half-a-million-dollar piece of equipment that looks like a long stretched-out chandelier …

“The technique could be used to fabricate computer chips that won’t get too hot while operating, or materials that can convert waste heat to energy. Computer chips are packed with billions of microscopic transistors that enable powerful computation, but …
