Other

“Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists have found that atomic disorder in certain boron-based hydrogen storage systems can potentially improve the rate of hydrogen uptake. Metal boride surfaces and their single-layer variants — known as borophenes — are generally thought to feature …

“As 3D printing continues to grow and evolve, diagnostics capable of monitoring builds in real-time have become essential tools for producing quality parts, particularly in emerging printing technologies such as Liquid Metal Jetting (LMJ). In LMJ, tiny molten metal droplets …
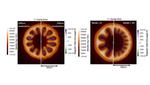
“Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers now have a better understanding on how strong the magnetic fields are in an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosion at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s most energetic laser. The researchers described …

“New research involving Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists shows that water can remain liquid in a metastable state when transitioning from liquid to a dense form of ice at higher pressures than previously measured. Water at extreme conditions has …

“While laser-based 3D printing techniques have revolutionized the production of metal parts by greatly expanding design complexity, the laser beams traditionally used in metal printing have drawbacks that can lead to defects and poor mechanical performance. Researchers at Lawrence Livermore …
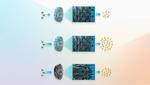
“To take advantage of the growing abundance and cheaper costs of renewable energy, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists and engineers are 3D printing flow-through electrodes (FTEs), core components of electrochemical reactors used for converting CO2 and other molecules to …

“Two-photon lithography (TPL) — a widely used 3D nanoprinting technique that uses laser light to create 3D objects — has shown promise in research applications but has yet to achieve widespread industry acceptance due to limitations on large-scale part production and time-intensive …

“Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have discovered that carbon nanotube membrane pores could enable ultra-rapid dialysis processes that would greatly reduce treatment time for hemodialysis patients. The ability to separate molecular constituents in complex solutions is crucial to many …
News Researchers measure electron emission to improve understanding of laser-based metal 3D printing

“Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have taken a promising step in improving the reliability of laser-based metal 3D printing techniques by measuring the emission of electrons from the surface of stainless steel during laser processing. Researchers collected thermionic emission …

“Alkaline water electrolysis has been touted as a path to establish a hydrogen economy by converting intermittent renewable energies into clean hydrogen-based chemical energy. However, current technology has achieved only low current densities and voltage efficiencies. To make electrolysis more …
