Other

“Perovskite particles could improve the performance of solar cells and light-emitting diodes via a simple process to stabilize the nanocrystal surface. A method for chemically stabilizing optical nanocrystals, without degrading their electrical properties, has been developed by scientists at KAUST …

“A new ink containing iron-oxide nanoparticles can be turned into fully printed and versatile components for cellular networks. Inkjet printing technology can be used to produce radio frequency devices, such as antennas, that can be magnetically reconfigured on demand. This …
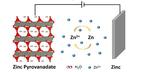
“A technique of microwave synthesis of layered oxides enables high-capacity aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Layered oxides can form the basis of high-performance materials for battery electrodes. A KAUST team has developed a cheap and simple technique that creates this crucial element …
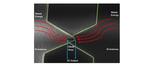
“Innovative diode design uses ultrafast quantum tunneling to harvest infrared energy from the environment. Most sunlight striking the Earth is absorbed by its surfaces, oceans and atmosphere. As a result of this warming, infrared radiation is emitted constantly all around …

“Fine tuning the composition of nitride alloys can further the development of optical and electronic interface devices. Controlling the electronic properties at the interface between materials could help in the quest for improvements in computer memory. KAUST researchers show that …

“An easy and reliable assembly approach, inspired by building blocks, challenges the current fabrication of electronic systems. A strategy for assembly of electronic systems—especially the flexible structures needed for high-performance devices of the future—uses integrated circuits as Lego-like …
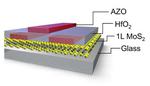
“See-through electronic devices, such as transparent displays, smart windows and concealed circuits require completely translucent components if users are to digitally interact with their perceived surroundings and manipulate this information in real time. Now, KAUST researchers have devised a strategy …
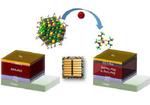
“The performance of solar cells that consist of semiconductor nanoparticles surrounded by ligand molecules is now easier to control. Researchers from KAUST have developed a method that enhances the ability of these colloidal quantum dot (CQD) solar cells to convert …
“Efficiency gains come from tuning the properties of semiconducting materials by combining layers of different composition. The electronic characteristics of an interface between two wide bandgap semiconductors are determined by researchers at KAUST: an insight that will help improve the …
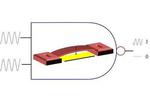
“A vibration-driven logic gate could form the basis for the next generation of efficient, low-power computers. Vibrating mechanical switches that can be cascaded to perform complex computational operations could take computing significantly further than today’s technologies. KAUST researchers have …
