Other

“Small tweaks in component ratios generate electronically different layers from the same material to create transparent transistors. Worldwide demand is growing for transparent conducting oxides for use in solar cells, flat panel displays, smart windows and semiconductor-based consumer electronics. KAUST …

“Working under the ocean is very difficult, even for automated machines, but a KAUST team is making great strides with an optical system for monitoring sensor locations. Extensive networks of underwater sensors—some attached to the seabed, some suspended in …

“Inkjet-printed switches make multiple frequency bands easier and cheaper to manage in wireless devices. Frequency-tunable communication modules, such as antennas and filters, are expected to help miniaturize wireless devices. Researchers at KAUST have created switches that enable control over these …

“New houses could soon deliver on a long-awaited promise and incorporate windows or roof tiles that harvest solar energy, research conducted at KAUST suggests. Derya Baran, at the KAUST Solar Center, and her colleagues have developed a photovoltaic organic material …

“The efficiency of solar cells can be increased by thin-film contacts developed by researchers at KAUST. Improving the performance of solar cells requires scrutinizing every aspect of their design. First, this means improving the crystalline quality of the absorbing material …

“A metal carbide within a hydrogel composite senses, stretches and heals like human skin for use in medicine and robotics. An electrically conductive hydrogel that takes stretchability, self-healing and strain sensitivity to new limits has been developed at KAUST. “Our …
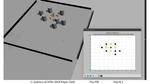
“Innovative drone designs and software enables a team of drones to work together in a coordinated approach. The software and hardware needed to co-ordinate a team of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that can communicate and work toward a common goal …

“An electronic tag that stretches and flexes while it records location and environmental data can monitor marine animals in their natural habitat. A thin smart patch called Marine Skin could make studying the behavior of marine animals easier and more …
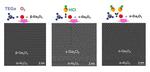
“Precise control of the atomic structure of gallium-oxide layers improves the development of high-power electronic devices. A simple method that uses hydrogen chloride can better control the crystal structure of a common semiconductor and shows promise for novel high-powered electronic …
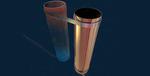
“Ultrathin films curve up into long, light and cost-effective heat-harvesting tubes for high-power generation. A system that can recycle excess heat into electricity could help meet the increasing energy demands of a growing global population. KAUST researchers have now engineered …
