Other

“Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip Millions of quantum bits are required for quantum computers to prove useful in practical applications. The scalability is one of the greatest challenges in the …

“Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich take an important step on the path towards topological quantum computers With their superior properties, topological qubits could help achieve a breakthrough in the development of a quantum computer designed for universal applications. So far, no …

“Perovskites are the great hope for further increasing the efficiency of solar modules in the future. Until now, their short service life has been considered the biggest hurdle to their practical use, but this could soon change. In the current …
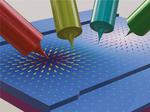
“Physicists at Forschungszentrum Jülich have made a significant step towards the realisation of new types of electronic components. Using a special four-tip scanning tunnelling microscope, they were able to directly measure the extraordinary electrical properties that exist in ultra-thin topological …
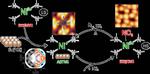
“Molecular interfaces formed between metals and molecular compounds have enormous potential as building blocks for future opto-electronics and spin-electronics devices. Transition metal phthalocyanine and porphyrin complexes are promising components for such interfaces. Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich, together with a team …

“Nanostructured material and a new cell design pave the way for the production of silicon solar cells with more than 26 percent efficiency There is no cheaper way to generate electricity today than with the sun. Power plants are currently …

“The quantum computer race is in full swing. Germany has long been one of the world leaders in basic research. An alliance between Forschungszentrum Jülich and the semiconductor manufacturer Infinion, together with institutes of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft (IAF, IPMS) as well …

“Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University have designed a circuit for quantum computers which is naturally protected against common errors Jülich, 18 February 2021 – Building a universal quantum computer is a challenging task because of the fragility of …

“In textbooks and explanatory videos, they are often depicted as colourful balloons or clouds: electron orbitals provide information on the whereabouts of electrons in molecules, a bit like fuzzy snapshots. In order to understand the exchange of electrons in chemical …
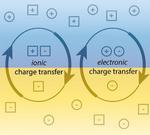
“Jülich researchers discover new formula for changing the electronic and magnetic properties of oxide interfaces (Advanced Materials) Most materials are either magnetic, or they are not. However, scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich have now discovered a new mechanism that allows for …

