Other

“How do you calculate the coordinated movements of two robot arms so they can accurately guide a highly flexible tool? ETH researchers have integrated all aspects of the optimisation calculations into an algorithm. The hot-wire cutter will be used …

“Electrons are able to move within molecules, for example when they are excited from outside or in the course of a chemical reaction. For the first time, scientists have now succeeded in studying the first few dozen attoseconds of this …
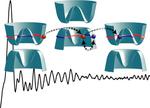
“In combined theoretical and experimental work, ETH physicists introduce and demonstrate a novel mechanism for electron optics in two-dimensional solid-state systems. The discovery opens up a route to engineering quantum-optical phenomena in a variety of materials and …

“ETH researchers at the Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering have developed a device that detects low concentrations of methanol in alcoholic beverages. The results are displayed on a smartphone wirelessly in real time. Methanol can be lethal, even if …

“Several technical advances have been achieved recently in the pursuit of powerful quantum computers. Now, Computer scientists from ETH Zurich have made an important breakthrough in the field of programming languages: their quantum language is the first of its kind …

“ETH researchers have developed a new method in which they use light to draw patterns of molecules that guide living cells. The approach allows for a closer look at the development of multicellular organisms – and in the future may even …
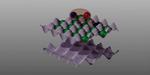
“In a material made of two thin crystal layers that are slightly twisted with respect to each other, researchers at ETH have studied the behaviour of strongly interacting electrons. Doing so, they found a number of surprising properties. Many modern …

“ETH physicists have developed the first high-repetition-rate laser source that produces coherent soft x-rays spanning the entire ‘water window’. That technological breakthrough should enable a broad range of studies in the biological, chemical and material sciences as well …

“With the help of machine learning, ETH researchers have developed a novel yet low-cost tactile sensor. The sensor measures force distribution at high resolution and with great accuracy, enabling robot arms to grasp sensitive or fragile objects. We humans …

“Researchers at ETH have produced a gel from cellulose fibres and biodegradable nanoparticles that liquifies when pressed through the nozzle of a 3D printer, but then quickly returns to its original shape. Their invention paves the way for personalised biomaterial …
