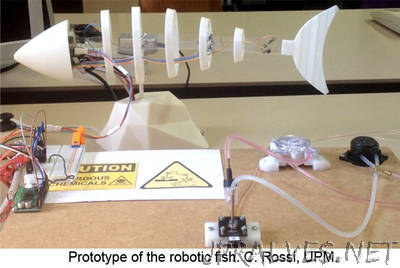
“Researchers from UPM and University of Florence are developing a bio-inspired robot equipped with special chemical sensors able to detect the pH of water. A group of researchers from Centre for Automation and Robotics (CAR CSIC-UPM) in collaboration with researchers from University of Florence are designing autonomous underwater vehicle with biosensors to monitor water quality. These robots, that mimic a swimming fish in order to minimize the fish disturbance and stress, can detect in-situ real-time anomalies and this is suitable to control environmental conditions in fish farms. Aquaculture has become the fastest growing animal food sector in the world. Today, the production of fish, crustaceans and shellfish supplies around fifty percentages of all fish that is consumed by humans globally. In order to keep aquaculture systems at an optimal level and to avoid physiological stress and disease of fish, water quality and adequate nutrition must be monitored and controlled.”
Link to article
