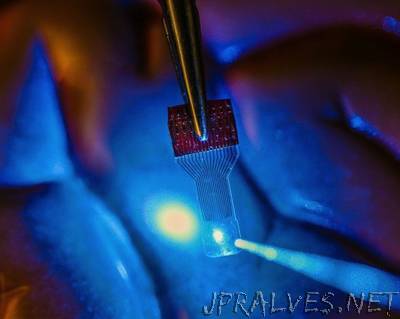
“Developing invisible implantable medical sensor arrays, a team of University of Wisconsin–Madison engineers has overcome a major technological hurdle in researchers’ efforts to understand the brain. The team described its technology, which has applications in fields ranging from neuroscience to cardiac care and even contact lenses, in the Oct. 20 issue of the online journal Nature Communications. Neural researchers study, monitor or stimulate the brain using imaging techniques in conjunction with implantable sensors that allow them to continuously capture and associate fleeting brain signals with the brain activity they can see. However, it’s difficult to see brain activity when there are sensors blocking the view.”
