Other

“Magnetic fields are used in various areas of modern physics and engineering, with practical applications ranging from doorbells to maglev trains. Since Nikola Tesla’s discoveries in the 19th century, researchers have strived to realize strong magnetic fields in laboratories …

“How do you test, in early-stage research, whether a potential pharmaceutical effectively targets a human tumor, organ, or some other part of the body? How do you grow a new hand or some other body part? Researchers are in the …
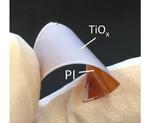
“Many common household items and devices have a coating that improves performance. For example, the thin Teflon coating on cookware helps prevent food from sticking to the surface. However, it’s difficult to prepare—at room temperature—the strongly adhering …
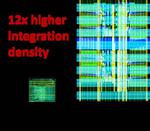
“Scientists at Osaka University built a new computing device from field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA) that can be customized by the user for maximum efficiency in artificial intelligence applications. Compared with currently used rewireable hardware, the system increases circuit density by …

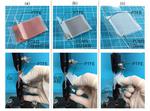
“A team of researchers from Osaka University and Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research developed the world’s thinnest and lightest magnetic sensor matrix sheet system that visualizes the two-dimensional distribution of magnetism on various surfaces. Conventional magnetic …

“A group of researchers at Osaka University developed a novel two-dimensional (2D) graphical tactile display to which one-dimensional (1D) adhesive information could be added by controlling adhesion of designated portions of the display surface. (Fig.1) Their research results were …
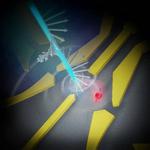
“A research team lead by Osaka University demonstrated how information encoded in the circular polarization of a laser beam can be translated into the spin state of an electron in a quantum dot, each being a quantum bit and a …

“A team at Osaka University has invented a new process for creating high-precision sensing devices that respond to the presence of hydrogen gas. By carefully controlling the deposition of metallic nanoparticles on a silicon surface, the researchers were able to …
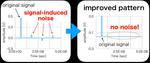
“In order to design noiseless electromagnetic (EM) devices, it is necessary to clarify the mechanism behind EM noise and theoretical calculations and computer simulations are performed for prediction assessment of devices. Two researchers at Osaka University developed an algorithm for …
“Polymers containing plastics are essential in modern life. Being lightweight, strong and unreactive, a vast range of technologies depend on them. However, most polymers do not adhere naturally to other materials, so they need adhesives or corrosive chemical treatments to …
