Other

“Researchers have made unparalleled ultrawide-bandgap semiconductors through temperature and timing, just like baking bread. Alloying, the process of mixing metals in different ratios, has been a known method for creating materials with enhanced properties for thousands of years, ever since …

“Flying drones connected by a cable tethered to a ground station could be a flexible solution for enhancing wireless connectivity in temporary hotspots. Keeping up with wireless demand is a never-ending endeavor for data providers, who often contend with temporary …
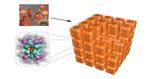
“Copper nanomaterials with a cubic shape so perfect that they form neatly aligned stacks when brought together have been created by researchers at KAUST. The cuboid copper nanoclusters, developed by rational design, are a new member of an exotic nanomaterial …

“Combining two light-absorbing materials and optimizing the flow of current improves the performance of solar cells. Two types of materials are better than one when it comes to solar cells, as revealed by an international team that has tested a …

“Catalyst nanoparticles trap an unprecedented range of wavelengths of light to convert carbon dioxide into methane. Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major driver of global warming, but this gas could also serve as a valuable resource. Researchers at KAUST …

“Sophisticated geometry design gives rise to a new form of crystalline material. A highly porous metal organic framework, assembled from molecular building blocks designed to lock together in a specific orientation, has been developed by researchers at KAUST. Metal organic …

“Computer models efficiently and accurately simulate the magnetic responses of ferrofluids by considering only the fluid’s surface. The spiky structure that erupts from the smooth surface of a ferrofluid when a magnet is brought close can be predicted more …

“Roads installed with wireless charging technology could become an integral feature of our cities in an electric vehicle future. By applying statistical geometry to analyzing urban road networks, KAUST researchers have advanced understanding of how wireless charging roads might influence …

“A single semiconducting material can produce white light by emitting light across the visible spectrum. The advantages of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), such as their tiny size, low cost and excellent power efficiency, mean they are found everywhere in modern life …

“A laser-based sensor developed at KAUST could improve monitoring of benzene emissions and limit exposure to this pollutant. In collaboration with Saudi Aramco, KAUST researchers have developed a device that accurately senses extremely low concentrations of benzene in real time …
